Railway

Whether it’s high-speed trains or local commuter lines, reliable cables keep the wheels of progress turning!
Railway cables play a crucial role in the efficient and safe operation of train networks. They are essential for transmitting power, data, and communication signals along railway lines. Over more than one million kilometres of railway cables are installed worldwide.
Measuring the electrical parameters of railway cables ensures reliable operation, safety, and compliance with electromagnetic compatibility standards. It enables engineers to design efficient and robust cable systems for modern rail networks.
- These cables are typically buried underground and serve various purposes in railway networks:
- Point Machine and Relay Circuits: Carry signalling data.
- Train-on-Track Circuits: Facilitate communication between trains and tracks.
- Signalling Speed Limit Indication Circuits: Provide vital indications (e.g., yellow light for low speed, double yellow light for even lower speed, and red/green lights for STOP/GO signals).
- Standard railway cables include:
- 10 Twisted Pairs (TWP)
- 6 quad Polyethylene Insulated Jelly Filled (PIJF) cables. The PIJF insulation makes them suitable for sub-soil deployment.
- ZPAU & ZPAU-SH Main Signaling Cables (AC Electrified Lines) for for example installation in intercity railways.
- ZPFU – Intercity railway signal cable (DC-electrified lines)
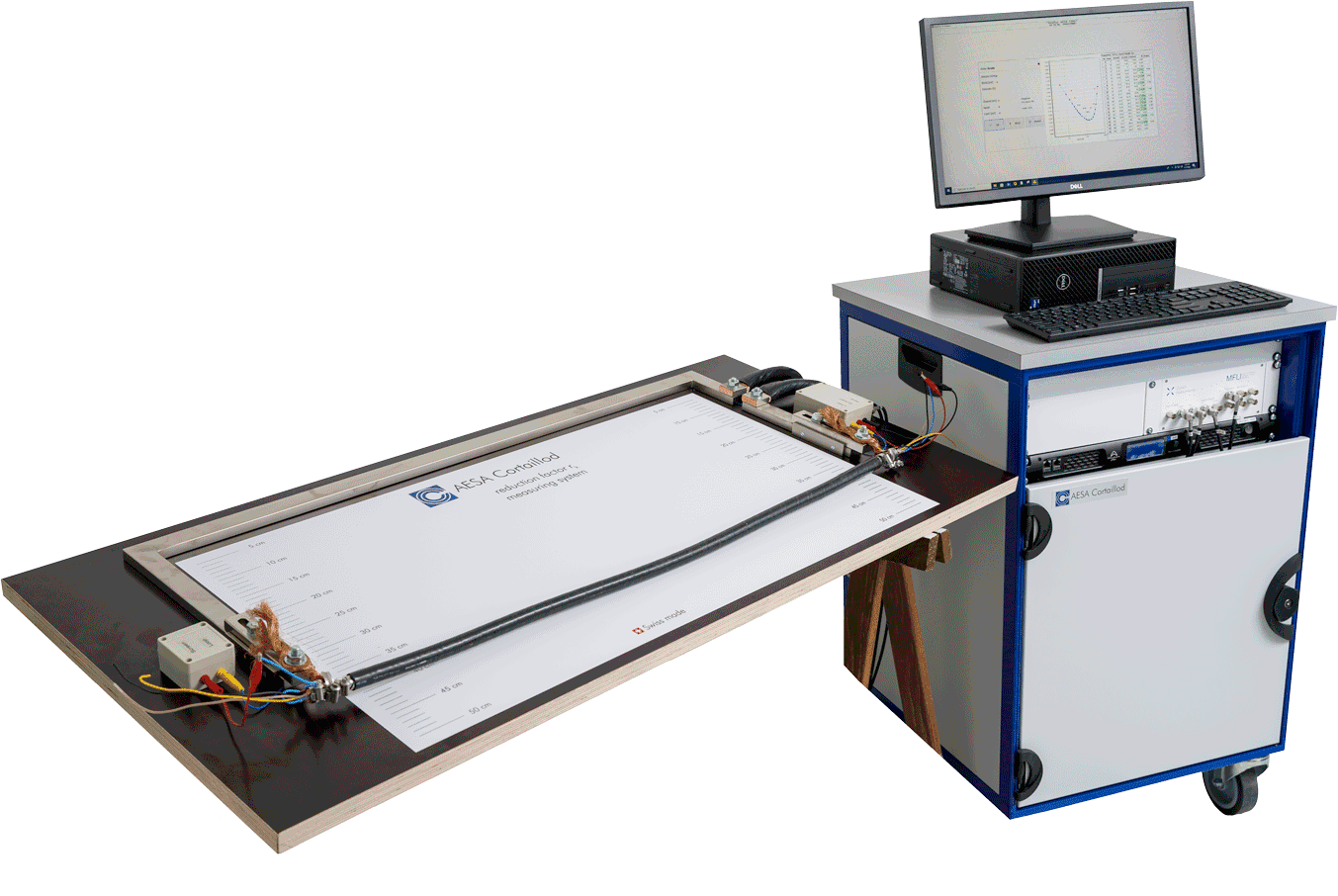
The reduction factor is a crucial design parameter for current trackside signalling cables. It indicates the cable’s level of protection against electromagnetic interference caused by catenary cables in high-speed train lines.
The AESA test system for reduction factor complies with major standards and allows for variable distances between the loop conductor and the cable under test.
Key features of the AESA test system to measure the reduction factor are:
- Fast and compliant measurement to prevent overheating of the cable sheath.
- Unique—currently the only automatic and complete solution available on the market.
- Controlled by software for full traceability and can be integrated with MES or ERP systems
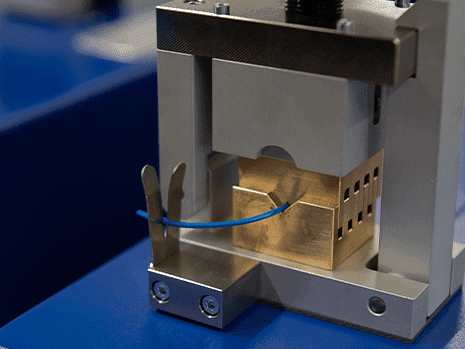
- Traction Power Cables:
- These cables supply power to electric locomotives, trams, and trains.
- Linear resistance testing ensures efficient power transmission and minimises energy losses.
- Traction power cables often have large cross-sectional areas due to high current requirements.
- Overhead Line Cables (Catenary Wires):
- These cables provide power to electric trains via overhead wires.
- Linear resistance testing ensures proper current flow and minimal voltage drop.
- Overhead line cables have unique designs and are subject to wear and environmental factors.
AESA has a complete product line of measurement instruments to measure such parameters. Additionally, our partners have direct access to our knowledge by making use of our dedicated Testing Laboratory.


- All
- Communication
- Energy
RestTest 50
Conductors up to 50 mm2
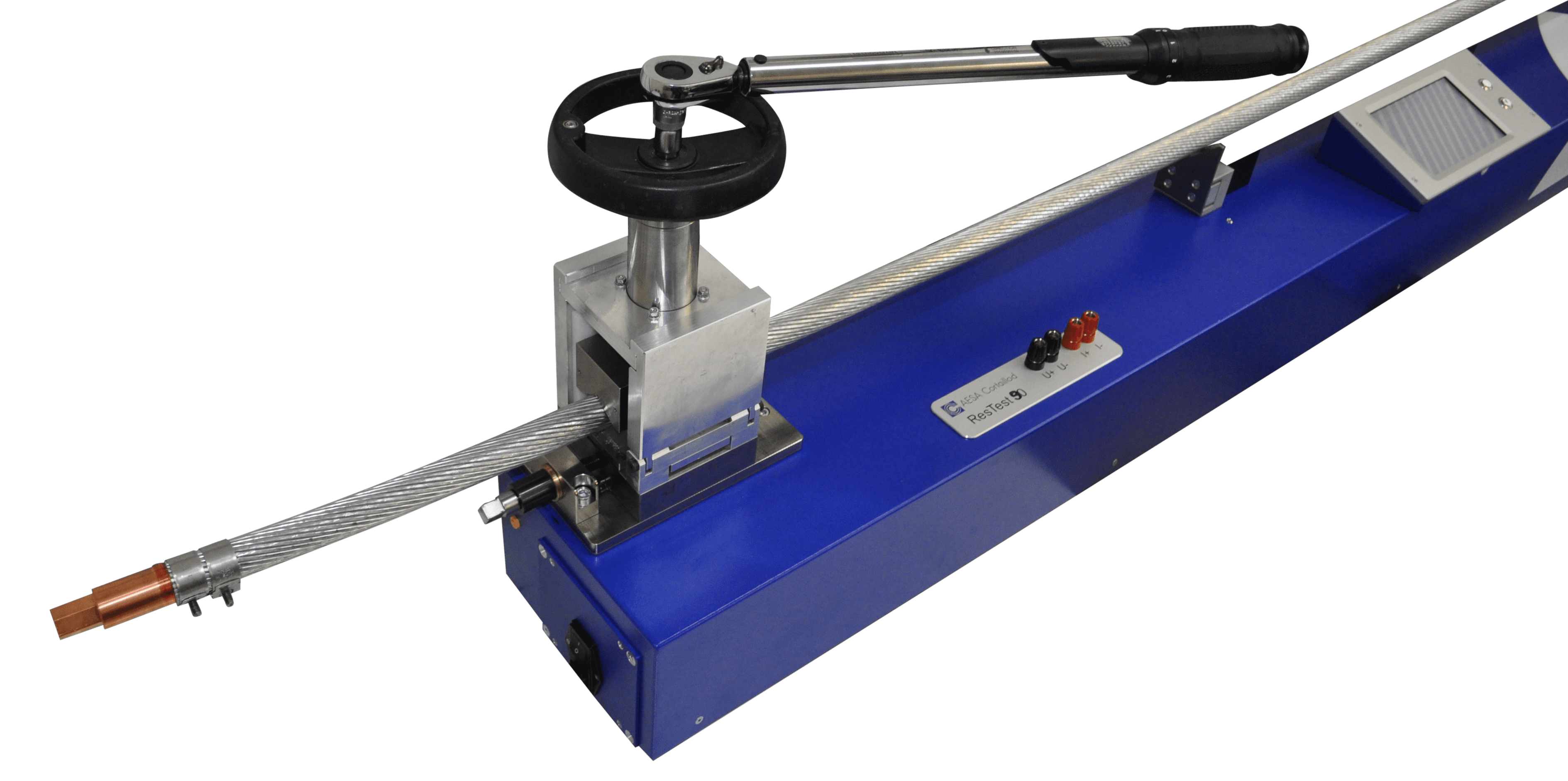
ResTest 90
Conductors up to 1,000 mm2
Puma
For RCKE intermediate tests
Reduction factor
Only automatic solution on the market
Semacare
Up to 64 pairs, 20 MHz
Testing Laboratory
For railway cable qualification